YONGNING
NEWS CENTER
Chain-type Chain Grate Description
Release Time:
Dec 08,2020
Wafangdian City Yongning Grate Manufacturing Co., Ltd.Founded in 1988, covering an area of 50,000 square meters, it is a professional manufacturer of boiler auxiliary machines designated by the state, located in southern Liaoning, south of Dalian, west of Bohai Bay, and east of the Shenda Expressway, with convenient transportation and a superior location.
Our factory can design and produce various grates according to user requirements to meet market needs. With strong technical strength and advanced and complete production equipment, we have laid a strong foundation for creating excellent products. For many years, we have supplied many domestic boiler manufacturers, and our products cover all over the country, with exports to neighboring countries such as Japan, Indonesia, and North Korea, receiving high praise.
Our main products: 40t/h—100t/h beam-type chain grates, 10t/h—80t/h large flake chain grates, 2t/h—40t/h small flake chain grates, 1t/h—20t/h chain belt chain grates, various slag discharge machines, coal feeding machines, grate reducers, layered coal bunkers, various boiler accessories, and we undertake various projects for the design, transformation, installation, and maintenance of grates.
"Quality as the foundation, sincerity to the world" is the purpose of our factory's development. Factory director Wang Conghui is willing to work hand in hand with new and old friends at home and abroad for sincere cooperation and mutual development.
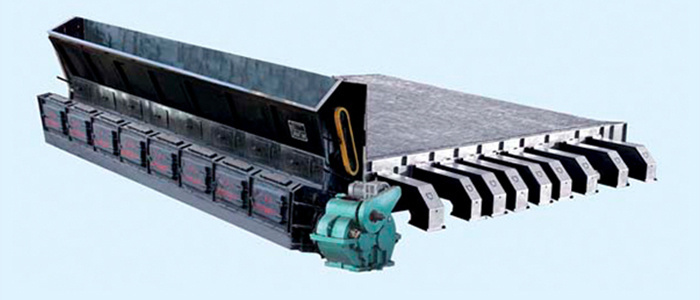
l Technical characteristics of chain belt grates
1. Scope of use and requirements
Chain belt chain grates are a mechanized layer combustion device that can be matched with boilers with an evaporation capacity of 0.5—20t/h and can also be used in various heating and drying equipment. They are suitable for burning bituminous coal, lignite, and peat. With special design, they can also be used as combustion equipment using raw materials such as bagasse, wood, and rice husks.
The coal quality used in this grate should meet the following requirements:
a. The maximum particle size of coal blocks should not exceed 40mm, and it is not suitable to burn coal dust below 0—5mm.
b. The moisture content of the coal should be less than 20%, preferably 8—10%.
c. The ash content of the coal should not exceed 30%, but should not be less than 10%, and the volatile matter should not be less than 20%.
d. The melting temperature of the coal ash should be greater than 1290.0C.
e. Caking property should not be strong.
f. The lower heating value of the coal should not exceed 4226kcal/kg.
g. If the above coal quality requirements conflict with the coal feeding settings, take the higher value of the two. The primary air temperature used in this grate should not exceed 200.0C.
2. Structural characteristics of chain belt chain grates:
Components: 1. Drive shaft; 2. Driven shaft; 3. Support; 4. Ash discharge device; 5. Air adjustment device; 6. Grate chain; 7. Coal feeding hopper; 8. Front wind door; 9. Side seal.
Technical characteristics:
a. Simple structure, low metal consumption, large ventilation cross-section ratio (about 12%); high strength and performance requirements for the main and driven shafts and grate plates.
b. Several independent air chambers are set along the longitudinal direction inside the grate, and the primary air entering the air chamber slows down due to diffusion and can evenly fill the air chamber. The air volume of each air chamber can be adjusted through the air adjustment device.
c. Ash discharge devices are arranged in each air chamber. At the bottom of the air chamber, ash discharge plates with ash discharge openings are arranged, and the movable doors connected to the ash discharge pull rods usually cover the ash discharge openings. By pulling the ash discharge handle at regular intervals, the ash falls from the ash discharge opening onto the grate chain below, which carries it to the ash collection hopper at the front or near the ash discharge door, where it is manually shoveled out.
d. The grate is debugged and operates normally in the factory, and the whole machine is shipped out. (It can also be shipped in parts according to user requirements.)
l Chain belt chain grate usage
1. On-site inspection and adjustment of the grate
This grate has undergone size adjustments and has passed an over 8-hour cold operation test in the factory. However, during transportation, vibrations may loosen the locking bolts, causing changes in structural size. Therefore, after the entire boiler installation is completed, the grate must be carefully inspected and subjected to a cold no-load test.
a. Check whether the adjustment screw of the drive shaft is loose. If it is loose, adjust the screw to tighten the drive bearing.
b. Fill the main and driven shaft bearings with lubricating oil.
c. Carefully check that no iron parts or other debris are lost or trapped anywhere in the grate.
d. Check whether the air adjustment device is flexible and troubleshoot any faults.
e. Check whether the ash discharge pull rod is flexible and troubleshoot any faults.
f. Check whether the coal gate rises and falls flexibly, and whether the distance between the left and right sides and the grate surface is equal.
g. The cover plate on the coal gate must be properly covered to prevent coal blocks from leaking in and jamming the coal gate, affecting the rise and fall.
h. After conducting the above inspections and adjustments, a cold operation test should be carried out. If any abnormal phenomena are found, stop the machine immediately, troubleshoot, and continue normal operation for more than 8 hours.
2. Ignition use
Open the ignition door, place the igniter inside, open the induced draft, after the igniter burns, manually add coal on top of the igniter. At this time, turn on the blower, and after the coal layer burns vigorously, close the ignition door, add coal to the coal hopper, intermittently operate the grate, and observe the ignition situation through the observation hole, making appropriate adjustments. Once the front arch is heated and the coal can ignite continuously, operate the grate and adjust the air volume to achieve normal combustion.
3. Grate operation management
a. The normal combustion condition on the grate is: the fire bed is flat, the flames are dense and uniform, presenting a bright yellow color, there are no cold air inlets, the burnout section is neat and consistent, and the ash is dark in color, with the smoke coming out of the chimney being light gray.
b. It is strictly forbidden to put iron or other debris into the furnace to prevent blocking the grate.
c. The coal layer should maintain a certain thickness, and only when the type of coal changes or the boiler load varies significantly should the thickness of the coal layer be adjusted. The thickness of the coal layer is generally 80-180mm. Bituminous coal utilizes a thin coal layer for combustion, with a thickness of 90-120mm. When burning bituminous coal or inferior bituminous coal mixed with anthracite, the coal layer thickness should be 100-130mm. If the coal is too wet, a thick coal layer should be used for slow combustion. (The above data is for reference only)
d. The coal bunker should not be lacking in coal, and the phenomenon of "coal bridging" in the bunker should be eliminated at all times.
e. When coal enters the furnace, it should ignite at a distance of 200-300 from the coal gate and should not burn under the coal gate, otherwise, it will damage the coal gate. If such a situation occurs, water can be added to the coal or the grate speed can be increased.
f. When coal enters the furnace, if it has not ignited at a distance of 200-300 from the coal gate, it is called "extinguishing fire". At this time, open the furnace door to stir the fire, that is, to push the burning coal to the coal layer near the coal gate, or add flammable materials to accelerate the ignition speed.
g. If coking is found, the coke block should not be less than 200mm; otherwise, the furnace door should be opened to break the coke.
h. The combustion on the grate should be kept uniform; if there are air inlets, black flames, or uneven coal layers, a fire poker can be used to level it.
i. The ash in the wind chamber and the front ash cleaning area of the grate must be cleaned 3-4 times per shift.
j. It is strictly forbidden to burn under positive pressure; at this time, the operation of the blower and induced draft should be checked, as well as whether the flue at the rear is blocked, and troubleshooting should be carried out.
k. "Choking the furnace" should be avoided as much as possible to prevent damage to the grate plates due to overheating.
l. When the boiler load increases and stronger combustion is needed, the induced draft should be increased first, then the blower, and then the grate speed should be increased. If necessary, the thickness of the grate should be increased. When the boiler load decreases and weaker combustion is needed, the air supply should be reduced first, and if necessary, the thickness of the coal layer can be reduced.
m. The shutdown of the grate is generally carried out in the following order.
1) Stop supplying coal half an hour in advance and reduce the grate speed.
2) Properly reduce the induced draft fan to allow the remaining burning coal on the grate to burn out before shutting down.
3) After burning out, stop the induced draft.
4) If necessary, the grate continues to operate to unload all the ash on the grate.
n. The emergency shutdown of the grate is carried out in the following order.
1) First stop the blower, then stop the induced draft.
2) Stop supplying coal.
3) Open the ignition door and quickly shovel away the unburned coal in front of the grate and the burning coal on the grate from under the ignition door.
4) Rotate the grate at the fastest speed to send all the ash and coal out of the furnace.
5) Shutdown.
4. Maintenance and repair of the grate.
1). Regularly add lubricants to the bearings on both sides of the main and driven shafts.
2). The grate must be adjusted to tighten the grate chain 4 times during the first month of operation at 3, 7, 15, and 30 days, and thereafter should be checked regularly. If the grate chain is found to be loose or misaligned, the adjustment screw at the front axle should be adjusted and the grate chain tightened in time to prevent arching.
3). If the grate gets stuck during operation, the fault should be eliminated in a timely manner according to the specific situation.
4). Grate plates that are burned out or deformed excessively should be replaced in a timely manner to avoid affecting operational safety.
5). During major repairs of the grate, check the wear of the sprockets, grate plates, front and rear shafts, supports, and base plates; if wear is severe, they should be replaced in a timely manner.
6). If the furnace is stopped for a long time, the coal in the bunker and the collected ash in each wind chamber should be cleared.
RELATED INFORMATION
How to choose a Manufacturer for grate production
Apr 01,2024
Precautions for Using the Grate
Mar 07,2024
The difference between reciprocating chain grate and biomass reciprocating grate.
Feb 15,2024
Photo News