YONGNING
NEWS CENTER
What is the structure and combustion process of a reciprocating grate?
Release Time:
Mar 16,2022
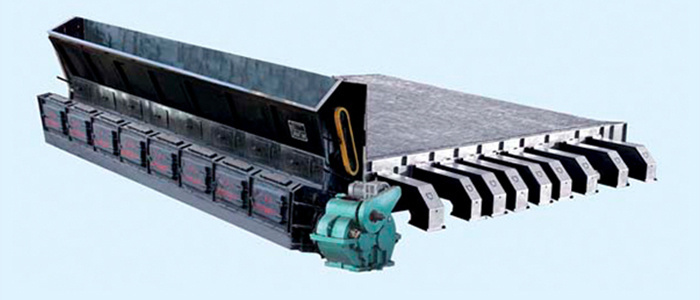
1. Structure of the Reciprocating Grate
Reciprocating GrateIt is also a commonly used furnace type for small and medium-sized cattle combustion devices. The reciprocating grate mainly consists of a fixed grate, a movable grate, a transmission mechanism, and a reciprocating mechanism.

The tail end of the movable grate bar is clamped on the movable beam, and its front end is directly laid on the adjacent next surrounding grate bar, making the entire grate bar appear distinctly trapezoidal and at a certain angle to facilitate the downward movement of the fuel. Each row of movable beams is connected into a whole with two channel steels, forming a movable frame. When the motor drives the eccentric wheel, which drives the push-pull rod connected to the frame, the movable grate moves back and forth with the movable frame, with a stroke of about 30-100mm and a reciprocating frequency of about 1-5 times/min, which can be adjusted by changing the motor speed. The tail end of the fixed grate bar is clamped on the fixed crossbeam, similar to the movable grate bar. Its front end is also set on the next adjacent grate piece, and a support rod is placed in the middle of the grate bar to reduce the pressure on the movable grate bar and the wear caused by reciprocating motion. The air required for combustion can be supplied through the longitudinal and transverse gaps between each layer of the grate. The ventilation cross-sectional area of the grate is about 7% to 12%. At the tail end of the inclined grate, the fuel falls into the ash pit after combustion.
2.Reciprocating GrateCombustion Process and Characteristics
The combustion process of the reciprocating grate is similar to that of the chain grate. The fuel falls from the hopper and enters the furnace through the adjusting door to adjust the thickness of the fuel layer. Under the reciprocating feeding action of the movable grate, the fuel slowly moves from front to back along the inclined surface of the grate, sequentially passing through various stages such as preheating and drying, volatile analysis ignition, coke combustion, and ash burnout. The new fuel at the top of the firebed is ignited and burned by the high-temperature flue gas and the radiation heat from the furnace arch. A major feature that distinguishes the reciprocating grate from the chain grate is the relative motion between the grate and the fuel. Due to the continuous raking action of the movable grate, some new fuel is pushed onto the hot bed below for combustion, artificially improving the ignition conditions. During the return process, the movable grate rakes the rear of the ignited carbon particles to the bottom of the non-fuel layer, becoming the ignition heat source for the bottom fuel. At the same time, the raking action loosens the fuel layer, increases permeability, promotes disturbance of the combustion bed, and the ash shell on the surface of the coke and fuel blocks is crushed or shed due to squeezing and flipping, which is beneficial for enhancing combustion and burnout. During operation, the feed amount of the reciprocating grate can be controlled not only by the height of the gate but also by adjusting the stroke and frequency of the movable grate.
Since the combustion process of the reciprocating grate still occurs in stages along the length of the grate, it is necessary to supply air in segments along the length of the grate. Generally, during normal operation, the air supply in the middle of the grate is large, and the corresponding air pressure is also high. The air supply in the front and rear sections is less, especially in the fuel preheating and drying section at the top of the firebed. To enhance the disturbance and mixing of the airflow in the furnace,Reciprocating Gratethe front arch, rear arch, or middle fire wall should still be set, and secondary air should be appropriately arranged to improve the ignition conditions of the fuel at the head of the firebed. In addition, the airflow in the furnace can be reasonably organized to allow the combustible gases generated at the front of the grate to flow above the high-temperature combustion zone, fully mixing with the excess air rising from the burnout zone, further enhancing burnout. The design and layout of the reciprocating grate are similar to that of the chain grate. The segmented air supply, secondary air arrangement, and arch layout and Size can refer to the design of the chain grate.
RELATED INFORMATION
How to choose a Manufacturer for grate production
Apr 01,2024
Precautions for Using the Grate
Mar 07,2024
The difference between reciprocating chain grate and biomass reciprocating grate.
Feb 15,2024
Photo News